METAL SPECIATION:
Terms and definitions (IUPAC Recommendations)
Chemical species are specific form of an element defined as to isotopic composition,
electronic or oxidation state, and/or complex or molecular structure.
Speciation analysis is the analytical activities of identifying and/or measuring
the quantities of one or more individual chemical species in a sample.
Speciation of an element, speciation is the distribution of an element amongst
defined chemical species in a system.
METAL SPECIATION: What for it is necessary?
• The toxicity, bioavailability and mobility of the metals in
aquatic ecosystems varies with its physico- chemical form;
• Individual metal species have a different chemical activity
and different ability to transformation;
• For forecasting of metal fate in aquatic ecosystems;
• For development of effective methods for water quality monitoring.
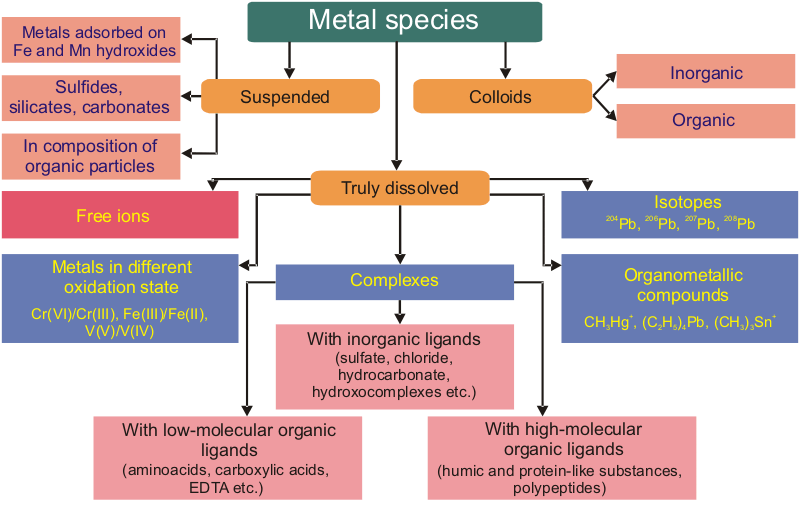
METAL SPECIATION: Structural aspects
The dissolved forms of trace metals are mainly present as free (hydrated) ions and complexes with a large variety of dissolved inorganic and organic matters. Free metal ions are regarded as the most toxic form. The complexing of HM with dissolved organic matter (DOM) known to be decreases their toxicity.
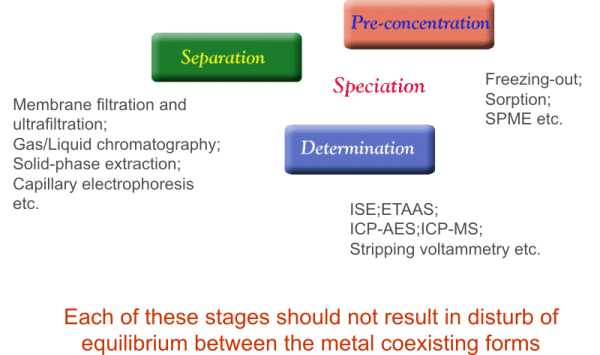
METAL SPECIATION: Tools
for investigation
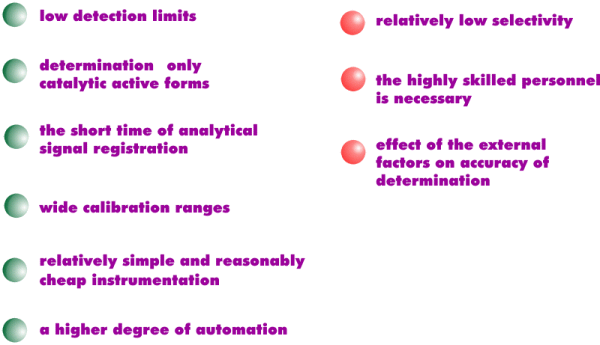
Chemiluminescent method: advantages and drawbacks
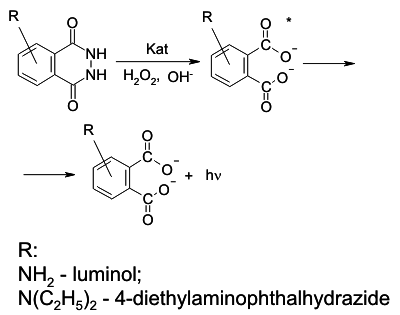
In our research we used CL method based on the catalytic effect of some metals in the
reactions between luminol or 4-diethylaminophthalhydrazide (4-DEAPH) and hydrogen
peroxide. The selectivity of metal detection can be achieved by changing pH of a
reaction mixture.
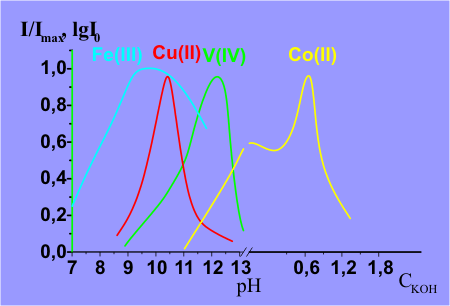
Chemiluminescent method in speciation analysis: application area
Determination of toxic species (free metal ions + labile complexes)
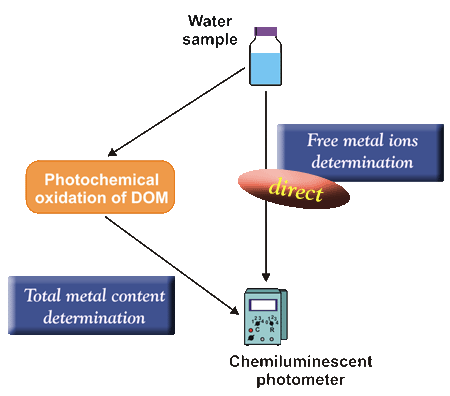
The chemiluminescent method enables
the direct determination
of free metal ions and labile complexes
without their preliminary separation.
Determination of metals in different oxidation states
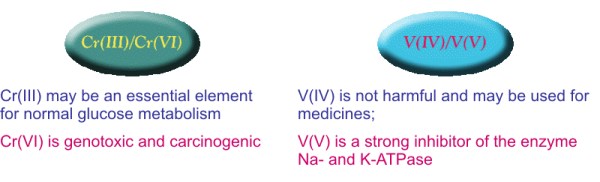
The chemiluminescent method allows to determine one of the
valent forms of these
metals
(Cr(III) and V(IV)) without their preliminary separation
Investigation of kinetic of metal species transformation
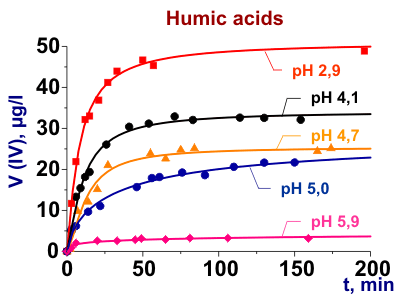
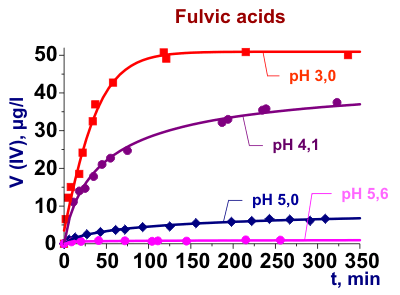
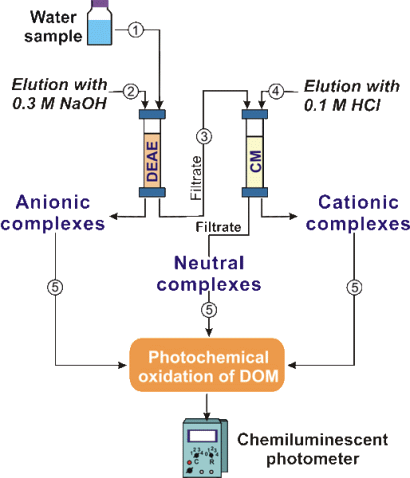
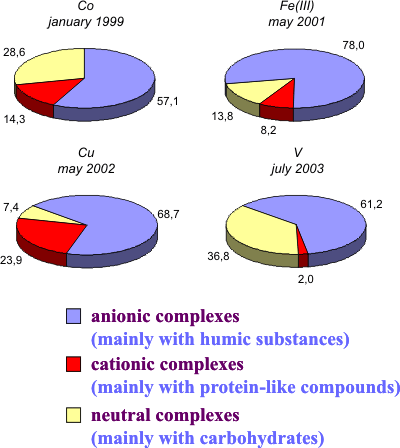
Investigation of the chemical nature of metal complexes with dissolved organic matters (DOM)
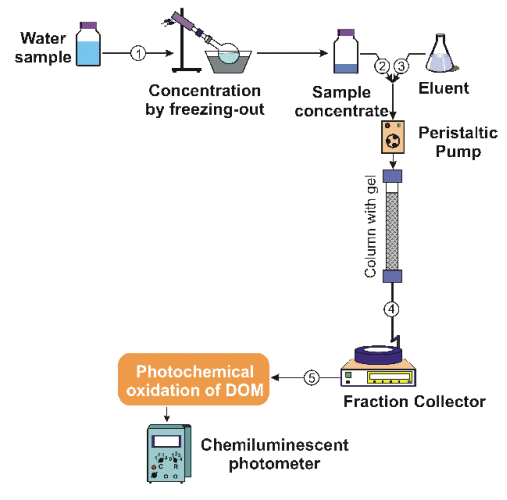
Determination of the molecular weight distribution (MWD)
of metal complexes with DOM
CONCLUSIONS:
• due to such characteristics as a low detection limits, short time of of analytical signal registration, species-selectivity, the chemiluminescent method is suitable for use in the speciation analysis;
• unlike the other methods of detection, i.g. spectroscopic,
the chemiluminescent method allows to determine directly the most toxic
forms of metals (free ions and labile complexes) without their preliminary
separation;
• combined with ion-exchange and gel-permeation chromatography
the chemiluminescent method is a powerful tool for the investigation of the coexisting forms
of metals in natural waters;
• to apply the described approach in speciation analysis more effectively
it is necessary to study thoroughly such a problem as on-line coupling of separation
technique with chemiluminescent detection.
| 